15.3_Template_in_Constant_Memory
15.3 Template in Constant Memory
Most template-matching applications perform many correlation computations with the same template at different offsets of the input image. In that case, the template statistics (SumT and fDenomExp) can be precomputed, and the template data can be moved to special memory or otherwise premassaged. For CUDA, the obvious place to put the template data is in constant memory so each template pixel can be broadcast to the threads computing correlation values for different image locations.
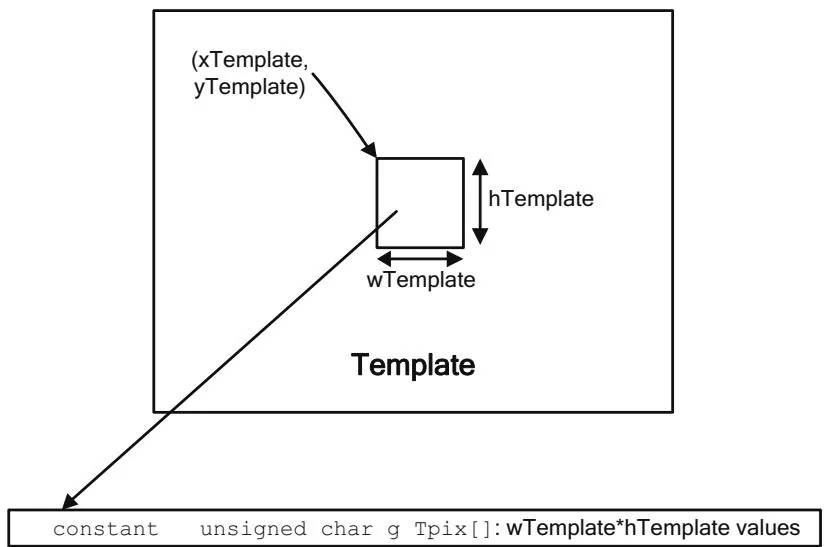
Figure 15.3 Template in constant memory.
The CopyToTemplate function given in Listing 15.3 pulls a rectangular area of pixels out of the input image, computes the statistics, and copies the data and statistics to constant memory.
Listing 15.3 CopyToTemplate function (error handling removed).
varaError_t
CopyToTemplate( unsigned char \*img,size_t imgPitch, int xTemplate,int yTemplate, int wTemplate,int hTemplate, int OffsetX,int OffsetY
1
{ CUDAError_t status; unsigned char pixels[maxTemplatePixels]; int inx $= 0$ . int SumT $= 0$ . int SumTSq $= 0$ . int cPixels $=$ wTemplate\*hTemplate; size_t sizeOffsets $=$ cPixels\*sizeof(int); float fSumT,fDenomExp,fcPixels;
CUDAMemcpy2D( pixels,wTemplate, img+yTemplate\*imgPitch+xTemplate, imgPitch, wTemplate,hTemplate,udaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaMemcpyToSymbol(g_Tpix,pixels,cPixels);
for (int i $=$ OffsetY;i $<$ OffsetY+hTemplate;i++) { for (int j $=$ OffsetX;j $<$ OffsetX+wTemplate;j++) { SumT $+ =$ pixels[inx]; SumTSq $+ =$ pixels[inx]\*pixels[inx]; poffsetx[inx] $= \mathrm{j}$ . poffsety[inx] $= \mathrm{i}$ . inx $+ = 1$ . }
} g_cpuSumT $=$ SumT; g_cpuSumTSq $=$ SumTSq;
CUDAMemcpyToSymbol(g_xOffset,poffsetx,sizeOffsets); CUDAMemcpyToSymbol(g_yOffset,poffsety,sizeOffsets);
fSumT $=$ (float) SumT; CUDAMemcpyToSymbol(g_SumT,&fSumT,sizeof(float));
fDenomExp $=$ float((double)cPixels\*SumTSq-(double)SumT\*SumT); CUDAMemcpyToSymbol(g_fDenomExp,&fDenomExp,sizeof(float));fcPixels = (float) cPixels;
cudaMemcpyToSymbol(g_cPixels, &fcPixels, sizeof(float));
Error:
return status;The corrTemplate2D() kernel given in Listing 15.4 then can read the template values from g_TPix[], which resides in constant memory. corrTemplate2D() is even simpler and shorter than corrTexTex2D(), since it does not have to compute the template statistics.
Listing 15.4 corrTemplate2D kernel.
global _void
corrTemplate2D_kernel(
float *pCorr, size_t CorrPitch,
float cPixels, float fDenomExp,
float xUL, float yUL, int w, int h,
int xOffset, int yOffset,
int wTemplate, int hTemplate)
{
size_t row = BlockIdx.y*blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
size_t col = BlockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
// adjust pointers to row
pCorr = (float *) ((char *) pCorr+row*CorrPitch);
// No _synchreads in this kernel, so we can early-out
// without worrying about the effects of divergence.
if (col >= w || row >= h)
return;
int SumI = 0;
int SumISq = 0;
int SumIT = 0;
int inx = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < hTemplate; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < wTemplate; i++) {
unsigned char I = tex2D(texImage,
(float) col+xUL+xOffset+i,
(float) row+yUL+yOffset+j);
unsigned char T = g_Tpix[inx++] ;
SumI += I;
SumISq += I*I;
SumIT += I*T;
}pCorr[col] = CorrelationValue( SumI, SumISq, SumIT, g_SumT, cPixels, fDenomExp ); }