7.3_Blocks_Threads_Warps_and_Lanes
7.3 Blocks, Threads, Warps, and Lanes
Kernels are launched as grids of blocks of threads. Threads can further be divided into 32-thread warps, and each thread in a warp is called a lane.
7.3.1 GRIDS OF BLOCKS
Thread blocks are separately scheduled onto SMs, and threads within a given block are executed by the same SM. Figure 7.1 shows a 2D grid of 2D blocks . Figure 7.2 shows a 3D grid of 3D blocks .
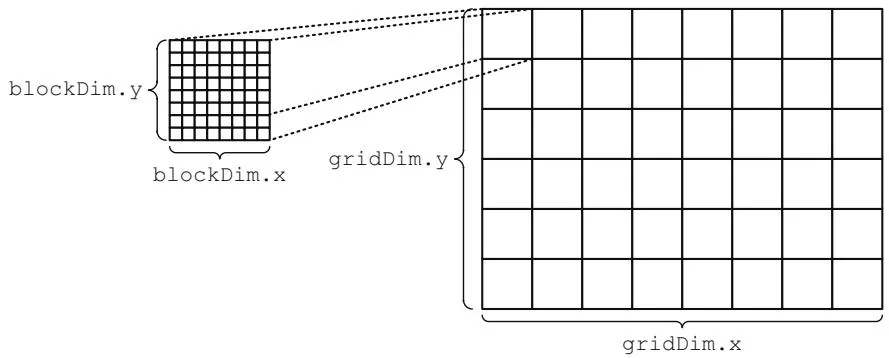
Figure 7.1 2D grid and thread block.
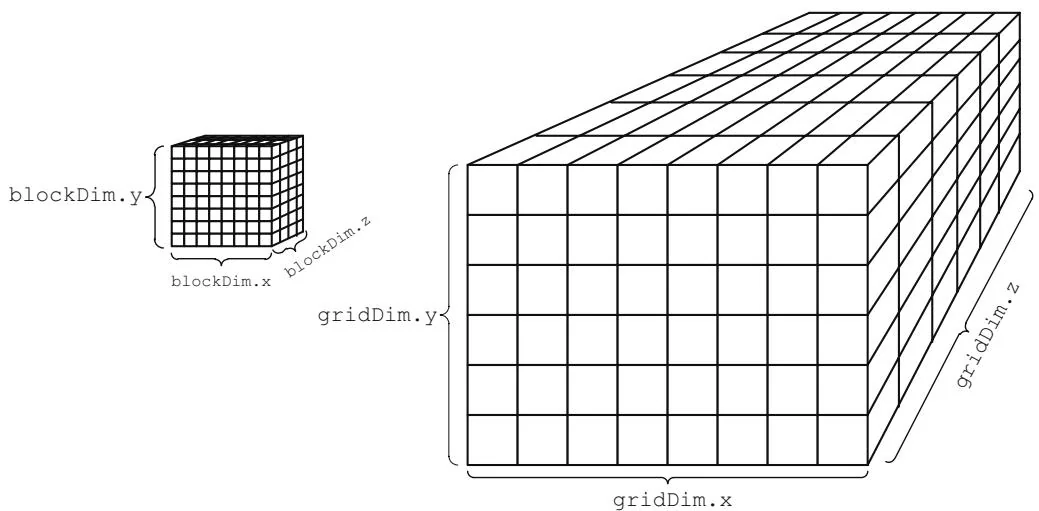
Figure 7.2 3D grid and thread block.
Grids can be up to 65535 x 65535 blocks (for SM 1.x hardware) or 65535 x 65535 x 65535 blocks (for SM 2.x hardware).5 Blocks may be up to 512 or 1024 threads in size,6 and threads within a block can communicate via the SM's shared memory. Blocks within a grid are likely to be assigned to different SMs; to maxi-
mize throughput of the hardware, a given SM can run threads and warps from different blocks at the same time. The warp schedulers dispatch instructions as needed resources become available.
Threads
Each threads gets a full complement of registers7 and a thread ID that is unique within the threadblock. To obviate the need to pass the size of the grid and threadblock into every kernel, the grid and block size also are available for kernels to read at runtime. The built-in variables used to reference these registers are given in Table 7.1. They are all of type dim3.