README
参考文献
第1阶段:自动微分
[1] Todd Young, Martin J. Mohlenkamp. Introduction to Numerical Methods and Matlab Programming for Engineers[M]. Athens: Ohio University, 2019.
[2] Wengert, Robert Edwin. A simple automatic derivative evaluation program[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1964, 7(8): 463-464.
[3] Automatic Reverse-Mode Differentiation: Lecture Notes.
[4] Automatic differentiation in pytorch.
[5] CS231n: Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition.
[6] Baydin, Atilim Gunes, et al. Automatic differentiation in machine learning: a survey[J]. Journal of machine learning research, 2018, 18(153).
[7] Maclaurin, Dougal. Modeling, inference and optimization with composable differentiable procedures[D]. Cambridge: Harvard University, 2016.
[8] unittest—�ニットテストフレムローク.
[9] Travis CI官网.
第2阶段:用自然的代码表达
[10] Hertz, Matthew, and Emery D. Berger. Quantifying the performance of garbage collection vs. explicit memory management[J]. Proceedings of the 20th annual ACM SIGPLAN conference on Object-oriented programming, systems, languages, and applications, 2005.
[11] PyPI. Memory Profiler.
[12] Python Document. contextlib.
[13] Wikipedia. Test functions for optimization.
[14] Christopher Olah. Neural Networks, Types, and Functional Programming.
[15] Yann LeCun. Differentiable Programming.
[16] PyTorch Document, TORCHSCRIPT.
[17] Swift for TensorFlow.
第3阶段:实现高阶导数
[18] Graphviz - Graph Visualization Software.
[19] Wikipedia, Rosenbrock function.
[20] PyTorch Document, torch.optim.LBFGS.
[21] Gulrajani, Ishaan, et al. Improved training of wasserstein gans[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems. 2017.
[22] Finn, Chelsea, Pieter Abbeel, Sergey Levine. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[J]. JMLR, 2017.
[23] Schulman, John, et al. Trust region policy optimization[J]. International conference on machine learning, 2015, 37: 1889-1897.
第4阶段:创建神经网络
[24] Seiya Tokui. Aggressive Buffer Release.
[25] LeCun, Yann A., et al. Efficient backprop[J]. Neural networks: Tricks
of the trade, 2012.
[26] Pascanu, Razvan, Tomas Mikolov, and Yoshua Bengio. On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks[J]. International conference on machine learning. 2013, 28:1310-1318.
[27] Duchi, John, Elad Hazan, and Yoram Singer. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2011, 12: 2121-2159.
[28] Zeiler, Matthew D. ADADELTA: an adaptive learning rate method[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1212.5701, 2012.
[29] Loshchilov, Ilya, and Frank Hutter. Fixing weight decay regularization in adam[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05101, 2017.
[30] Chainer MNIST Example.
[31] PyTorch MNIST Example.
[32] Chainer Document. Link and Chains.
[33] TensorFlow API Document. Module: tf kerasoptimizers.
第5阶段:DeZero高级挑战
[34] Srivastava, Nitish, et al. Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. The journal of machine learning research 2014: 1929-1958.
[35] Ioffe, Sergey, Christian Szegedy. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.03167, 2015.
[36] Simonyan, Karen, Andrew Zisserman. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556, 2014.
[37] He, Kaiming, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[R]. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition. 2016.
[38] Iandola, Forrest N., et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and MB model size[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1602.07360, 2016.
[39] SPHINX documentation.
[40] ONNX官网.
[41] Goodfellow, Ian, et al. Generative adversarial nets[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems. 2014.
[42] Kingma, Diederik P., Max Welling. Auto-encoding variational bayes[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6114, 2013.
[43] Gatys, Leon A., Alexander S. Ecker, and Matthias Bethge. Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks[R]. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016.
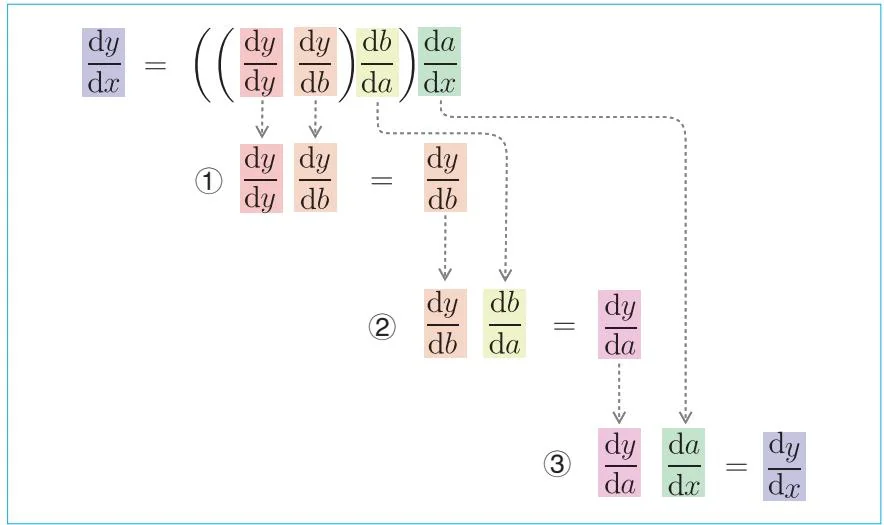
图5-2 从输出端的导数开始依次进行计算的流程
图25-2 改变节点的颜色
图25-3 圆形(椭圆形)和矩形节点的例子
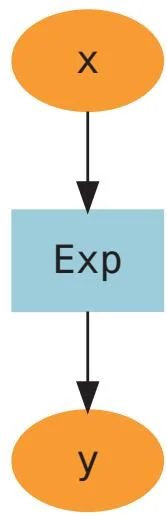
图25-4 有箭头连接的节点
图26-1 计算图可视化的示例
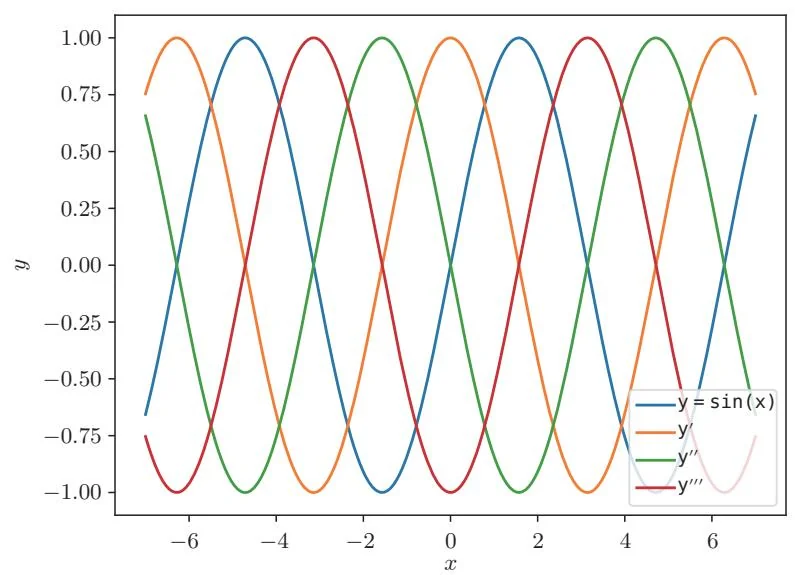
图34-1 y=sin(x)及其高阶导数的图像(标签y'对应一阶导数,y''对应二阶导数,y''对应三阶导数。)

微信连接

回复“深度学习”查看相关书单

微博连接
关注@图灵教育 每日分享IT好书
图灵社区
iTuring.cn
在线出版,电子书,《码农》杂志,图灵访谈
深度学习入门②:自制框架
“鱼书”《深度学习入门:基于Python的理论与实现》作者又一力作。带你创建深度学习框架,直击现代深度学习框架本质!
本书有什么特点?
简明易懂,讲解详细
本书延续前作的行文风格,采用通俗的语言和大量直观的示意图详细讲解,帮助读者加深对PyTorch、TensorFlow和Chainer等现代深度学习框架的理解,进一步巩固Python编程和软件开发的相关知识。
通过“从零创建”,剖析深度学习框架机制
本书会从零创建一个深度学习框架,让读者在运行程序的过程中了解深度学习框架中蕴藏的技术与机制。通过这样的体验,读者可看清深度学习框架的本质。
增量开发
本书将繁杂的深度学习框架的创建工作分为60个步骤完成,内容循序渐进,读者可在一步步的实践过程中获得正向的反馈结果,激发学习动力。
图灵社区:iTuring.cn
分类建议 计算机/人工智能
人民邮电出版社网址:www.ptpress.com.cn
O'Reilly Japan, Inc.授权人民邮电出版社有限公司出版
此简体中文版仅限于在中华人民共和国境内(不包括香港特别行政区、澳门特别行政区及台湾地区)销售发行
This Authorized Edition for sale only in the People's Republic of China (excluding Hong Kong SAR,
Macao SAR and Taiwan)

扫码领取随书代码资料

定价:129.80元